Studying smarter—not longer—is the key to academic success. Whether you’re a high school student, a college undergrad, or preparing for a certification exam, effective study techniques can help you absorb information more efficiently, retain it longer, and reduce stress. But with so many tips and hacks floating around, how do you know what really works?
Here are 10 study techniques backed by research and real-world success that can make a genuine difference in your learning routine.
1. Use Active Recall
One of the most effective methods of studying is active recall. Instead of passively rereading notes or textbooks, test yourself on the material. Try closing your book and asking yourself: “What did I just learn?” or use flashcards to quiz yourself. The act of retrieving information strengthens neural connections and helps move knowledge into long-term memory.
2. Embrace Spaced Repetition
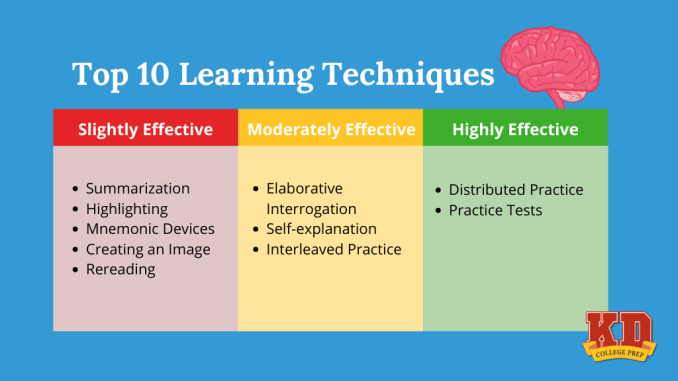
Rather than cramming the night before an exam, space your review sessions over time. This method, called spaced repetition, uses gradually increasing intervals to revisit material. Tools like Anki or Quizlet are excellent for this technique, helping you remember information more effectively than repeated massed studying.
3. Apply the Pomodoro Technique
Productivity experts swear by the Pomodoro Technique—25 minutes of focused study followed by a 5-minute break. After four “Pomodoros,” take a longer 15–30-minute break. This method keeps your brain fresh, reduces burnout, and helps you maintain consistent progress without feeling overwhelmed.
4. Teach What You’ve Learned
One of the best ways to check your understanding is to try teaching the concept to someone else. This technique, often called the Feynman Technique, forces you to simplify and clarify the material. If you struggle to explain it clearly, you likely need to revisit that topic.
5. Mix Up Your Study Environment
Studying in the same spot every time can cause your brain to associate information too narrowly with that location. Try switching environments occasionally—study at the library, a park, a different room, or even a quiet café. These small changes can enhance memory by creating different contextual cues.
6. Use Interleaved Practice
Instead of focusing on one subject or problem type at a time, interleaving involves mixing different topics or skills within a single study session. For example, when studying math, alternate between algebra, geometry, and word problems. This technique improves your ability to transfer knowledge and apply it flexibly in different contexts.
7. Take Handwritten Notes
Although typing may be faster, handwritten notes can promote deeper processing of information. Writing forces you to summarize and organize ideas, which improves comprehension and memory retention. When revising, rewrite key concepts in your own words to reinforce your understanding.
8. Use Visual Aids and Mind Maps
Visual learners benefit greatly from charts, diagrams, and mind maps. These tools allow you to organize complex information spatially, showing relationships between concepts. Creating your own visuals makes you engage more actively with the material and can be a great complement to textual notes.
9. Eliminate Distractions
Distraction is the enemy of effective studying. Turn off notifications, close irrelevant tabs, and put your phone on silent or in another room. If you find yourself distracted often, consider using website blockers like Freedom or StayFocusd. A distraction-free environment allows your brain to focus entirely on learning.
10. Set Specific Goals and Track Progress
Don’t just sit down with a vague intention to “study.” Set clear, actionable goals for each session, such as “review chapters 3 and 4” or “complete 20 flashcards.” Use a planner or app to track your goals and progress over time. Monitoring your growth keeps you motivated and helps you adjust strategies as needed.