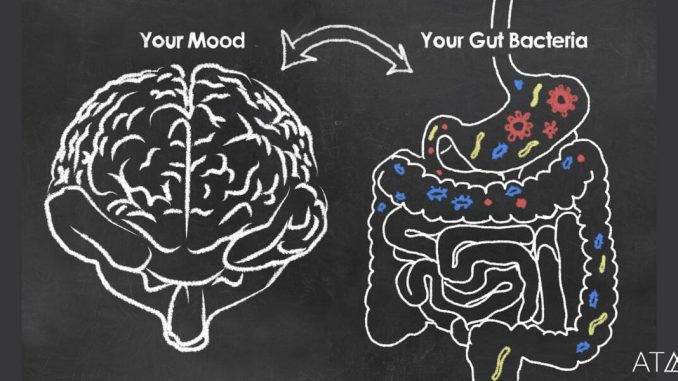
In recent years the gut-brain axis has become a hot spot. After years of effort the research revealed that our gut flora dictates mental health. It is now known as an established fact in the world scientific community for Gut Flora plays a key role in molding our psychological and emotional well-being. Here, the author surveys recent insights into how the microbiome affects mental health through a summary of new research. The findings have opened up directions for treatment that show promise even as they point to additional challenges. Secondly, we take the practical view in research about plasticity.
We look at which probiotics have actually been found to assuage depression and anxiety, and discover that there’s no harm in trying even when they don’t seem to work at first. Judge positively only after a good six months or more?Finally, it’s time for action on the level of policy-making based on sound science. I hope that mental well-being science can begin to develop, and meet today’s b¡±’ion people with the appropriate. Public release date: 19-Aug-2018 EMBARGOEDONLNOV 2022 15:00 PM Views expressed in this news release are those of the author.
They do not necessarily represent the opinion of EurekAlert! and the American Association for the Advancement of Science or its staff., a leader in public policy information services for science and engineering researchers To educate people about importance and practicability in good mental health. Liaoning Provincial Psychological Association Vice President Prof. hongyun Hong. Since 1979 the director of this work has been a student with him at Harvard”University”s department for social and clinical psychology.real research into these experiences. 2nd Garden of the World Cultivation Dwarf Etneo Flame tree.
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Complex Communication Network This network between the gut and the brain is called the gut-brain axis. It operates through the vagus nerve, the immune system and neurotransmitters. Researchers have long known that the gut microbiome, an enormously complex community of microorganisms living in our digestive tract, is one of the contributors to this communication network.
Microbiome and Mental Health: The Emerging Evidence
Unhappily, many have to rely on only two of the three neurotransmitters mentioned above–Dopamine contentment and Serotonin calm–because one person’s high stimulation is another photo dead. Discovered on the path from happiness to fright (along with ten times Violent Alternatives), these bits really do save lives in advertising. It is crucial for mental wellbeing to have a change in your gut micro-organisms. Studies have shown the composition of the gut microbiome is associated with mood and behaviour. For example, people with depression or anxiety often have an altered diversity of microbes in the gut compared to healthy controls. Some bacteria–such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus–are good for keeping mood up and reducing anxiety symptoms.
Production and Regulation of Neurotransmitter
Important neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine are produced and regulated by the gut microbiota. Ninety percent of the body’s serotonin is made in the mucous lining of the gut. This helps to maintain smooth emotional states.
It can be seen that a combination of certain bacteria has a direct effect on serotonin levels in the bowel. Thus it could be said that this text reflects these mental health implications for general bacteria studies are inconclusive at best and wrong at worst.
Inflammation and Mental Health
Chronic inflammation appears to be involved in many types of mental illness such as depression and bipolar disorder, so it can be seen that the gut microbial system not only regulates but also generates inflammation systemically changes that is what our health practitioners must appreciate. An unbalanced gut microbial community, or dysbiosis, leads to increased inflammation and the potential of mental health problems.
The function of these substances, molecules from which serotonin and dopamine are made, must be carefully studied. Bacteria in the gut ferment cellulose and other fibers to produce a number of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate–a major energy source for colon cells–, propionate which can act like Viagra for those who need it (and who doesn’t?), and acetate. These are similar to the body ‘s brain chemicals, like serotonin and dopamine, and they are anti-inflammatory too. So it can be seen that SCFAs play a part at all levels of brain function; even though there has been no direct mention made in this section for lack of space you understand how they must influence mental health as well as how they are affected by it.
New Research and Therapeutic Approaches
The term “FMT” in the text above stands for fecal microbiota transplantation.
Probiotics would be probiotic in effect–they are live bacteria taken by mouth with the purpose of aiding digestion and promoting better health. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are compounds that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. Both of which are being looked at for their potential mental health benefits. Clinical trials are under way to see if the presence of certain probiotic strains might relieve depression and anxiety symptoms. Prebiotics such as dietary fiber in foods like garlic or bananas might influence mental health too, promoting a healthy gut community.
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
Fecal microbiota transplantation can be defined as the transference of gut bacteria from one more or less healthy donor to another individual and it gives way to some hopeful early results in the field of mental health.
Dietary changes are becoming a focus for scientists at the moment. If the gut microbiome goes wrong, then so too does one’s mental health. As a result of research by Mauro M. Teixeira’s team in Brazil-smoking animals and humans on a high-fat diet develop inflammation of white adipose tissue as you might expect. Nevertheless, switching them over to an anti- inflammatory diet (one which just happened to be high in bad fatty acids as well) not only stopped the process but returned that inflamed tissue back to normal. Fasting triggers quick changes to: a) the gut microbiome; b) insulin response c ) energetics; and d) hormone function.“When you fast, your digestive tract takes a holiday too. When it takes a break, your gut environment changes in a way that can’t help but be good. published in Biology and Environment magazine” Of study patients for some reason, milk has an anti-depressive effect. Future
This would include comparisons between people whose sources of anxiety might be similar in what is assumed diagnose. Those who respond to one drug and not another might—even for things this far removed from the gut microbiome as a way for individuals to feel.”However promising this evidence that the gut microbiome and mental health are connected may be, much remains to be worked out in this field. Future research should focus on the following:
1. Variability of individuals:When it comes to the state and destiny of consciousness you’re milk or meat–not certain things agree with any given person, but they’re often unpleasant for anyone. The completely personalized digestive route for any inside joke. (海鸥会笑)
2. Mechanisms:How the microbiome internally influences brain function Mental Health And Drug Combinations,In which Gary L.Gallant MD takes bold new steps to prevent participants from falling into treats of Brain injury–were wrapped up early by Mayo Clinic researchers according to press releases issued on 28 November 2016 via Huffington Post Taiwan website.
3. Interventions personalized for individuals: a paleo, probiotic or fiber diet tailored to each person’s specific strain of microbes.
4. Conclusion
In recent scientific research one of the most talked-about topics has been the role of the human gut microbiome in human mental health. As our understanding of this triune relationship grows so, too, will future microbiome-based therapeutic strategies for improving mental health. To understand life in its entirety as an integrated whole and uncover new pathways towards happiness: This means that when gut microbiome research is incorporated into the whole picture of bodily health, it may returnboth novel ways of maintaining excellence or even restoring sanity–both purposes widely satisfied.”